New research shows cannabis heals broken bones and prevents rejection of transplanted organs
by Justin Gardner, Intellihub
The medical uses of cannabis and its derivatives are continuing to be discovered at an astonishing rate. This is despite the fact that U.S. government clings to an absurd, baseless classification of cannabis as a Schedule I drug, which severely limits research and scientific advancement.
We can add bone fractures and organ transplants to the diverse list of conditions that medicinal cannabis can treat.
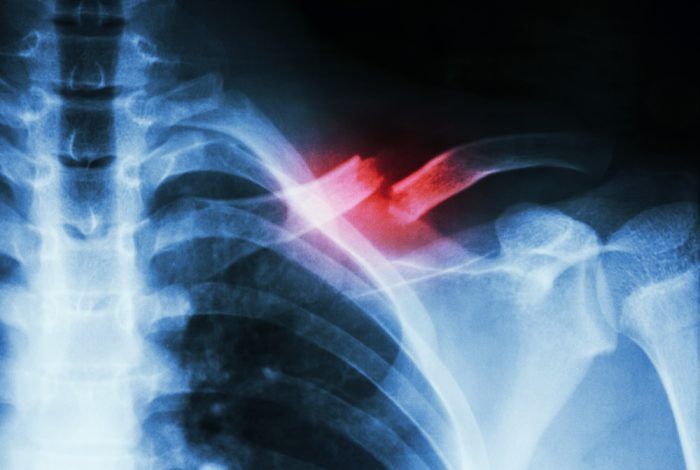
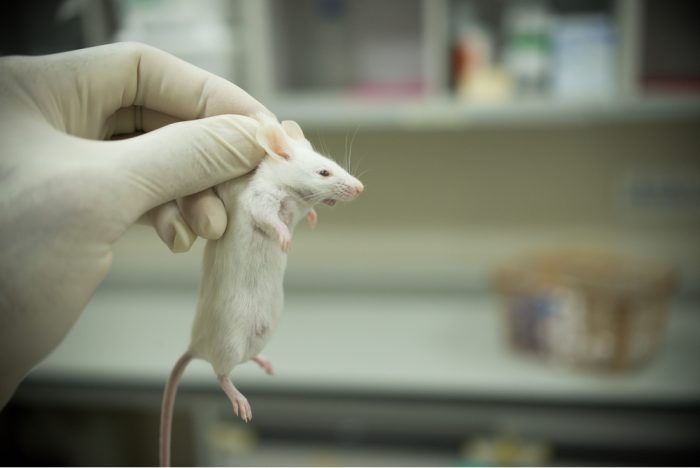
A study performed by Tel Aviv University and Hebrew University researchers finds that the non-psychotropic component cannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) helps heal bone fractures. They administered the compound to rats with mid-femoral fractures and found that it “markedly enhanced the healing process of the femora after just eight weeks.”
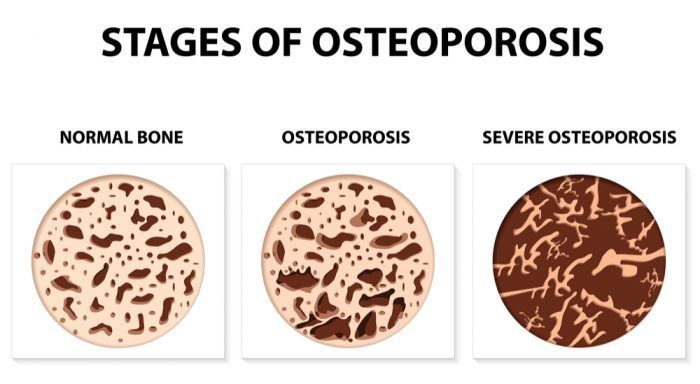
The team had found in earlier research that our bodies’ cannabinoid receptors stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone loss. It was a natural progression to test how this can be utilized to aid bone healing.
“The clinical potential of cannabinoid-related compounds is simply undeniable at this point,” said Dr. Gabet. “While there is still a lot of work to be done to develop appropriate therapies, it is clear that it is possible to detach a clinical therapy objective from the psychoactivity of cannabis. CBD, the principal agent in our study, is primarily anti-inflammatory and has no psychoactivity.”
Back in the U.S., researchers at the University of South Carolina School of Medicine discovered another new field of cannabis treatment. They found that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active ingredient in cannabis, can delay the rejection of incompatible organs.
The research performed in mice provides clear justification for its testing in clinical trials. If THC can be used to prevent organ rejection, as the authors suggest is possible, it can literally save lives. Again, the work focuses on cannabinoid receptors.
“More and more research is identifying potential beneficial effects of substances contained in marijuana, but a major challenge has been identifying the molecular pathways involved,” said John Wherry, Ph.D., Deputy Editor of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology. “These new studies point to important roles for the cannabinoid receptors as targets that might be exploited using approaches that refine how we think about substances derived from marijuana.”
Scientists around the world are resuming the exploration of medical cannabis that was interrupted in the 1930s and ‘40s by irrational government prohibitions. We are only just discovering its usefulness in treating epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, cancer and multiple sclerosis.
For centuries, cannabis was used as a medical remedy. The tools of modern medicine are now allowing extraordinary insights into this plant and the powerful capabilities of cannabinoid receptors.
Despite the amazing benefits of this plant, in police state USA, police officers will kill you for it - and they will call it "justice."
by Justin Gardner, Intellihub
The medical uses of cannabis and its derivatives are continuing to be discovered at an astonishing rate. This is despite the fact that U.S. government clings to an absurd, baseless classification of cannabis as a Schedule I drug, which severely limits research and scientific advancement.
We can add bone fractures and organ transplants to the diverse list of conditions that medicinal cannabis can treat.
A study performed by Tel Aviv University and Hebrew University researchers finds that the non-psychotropic component cannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) helps heal bone fractures. They administered the compound to rats with mid-femoral fractures and found that it “markedly enhanced the healing process of the femora after just eight weeks.”
The team had found in earlier research that our bodies’ cannabinoid receptors stimulate bone formation and inhibit bone loss. It was a natural progression to test how this can be utilized to aid bone healing.
“The clinical potential of cannabinoid-related compounds is simply undeniable at this point,” said Dr. Gabet. “While there is still a lot of work to be done to develop appropriate therapies, it is clear that it is possible to detach a clinical therapy objective from the psychoactivity of cannabis. CBD, the principal agent in our study, is primarily anti-inflammatory and has no psychoactivity.”
Back in the U.S., researchers at the University of South Carolina School of Medicine discovered another new field of cannabis treatment. They found that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the active ingredient in cannabis, can delay the rejection of incompatible organs.
The research performed in mice provides clear justification for its testing in clinical trials. If THC can be used to prevent organ rejection, as the authors suggest is possible, it can literally save lives. Again, the work focuses on cannabinoid receptors.
“More and more research is identifying potential beneficial effects of substances contained in marijuana, but a major challenge has been identifying the molecular pathways involved,” said John Wherry, Ph.D., Deputy Editor of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology. “These new studies point to important roles for the cannabinoid receptors as targets that might be exploited using approaches that refine how we think about substances derived from marijuana.”
Scientists around the world are resuming the exploration of medical cannabis that was interrupted in the 1930s and ‘40s by irrational government prohibitions. We are only just discovering its usefulness in treating epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, cancer and multiple sclerosis.
For centuries, cannabis was used as a medical remedy. The tools of modern medicine are now allowing extraordinary insights into this plant and the powerful capabilities of cannabinoid receptors.
Despite the amazing benefits of this plant, in police state USA, police officers will kill you for it - and they will call it "justice."
Last edited: